What Causes Feet To Over Pronate
OverviewExcessive pronation hampers our natural walking pattern, causing an imbalance and leading to wear and tear in other parts of the body, with every step we take! Whether you have a true flat foot or suffer from over-pronation in both cases your poor walking pattern may contribute to a range of different complaints. Especially with age, poor alignment of the feet will cause very common conditions such as heel pain or knee Pain.
Causes
Generally fallen arches are a condition inherited from one or both parents. In addition, age, obesity, and pregnancy cause our arches to collapse. Being in a job that requires long hours of standing and/or walking (e.g. teaching, retail, hospitality, building etc) contributes to this condition, especially when standing on hard surfaces like concrete floors. Last, but not least unsupportive footwear makes our feet roll in more than they should.
Symptoms
Overpronation can be a contributing factor in other lower extremity disorders, such as foot pain, plantar fasciitis, ankle injuries, medial tibial stress syndrome (shin splints), periostitis, stress fractures and myofascial trigger points. Overpronation increases the degree of internal tibial rotation, thereby contributing to various knee disorders such as meniscal injury or ligament sprains. The effects of the postural deviation are exaggerated in athletes due to the increase in foot strikes while running and the greater impact load experienced. When running, three to four times the body weight is experienced with each foot strike.2 If overpronation exists, the shock force is not adequately absorbed by the foot and is transmitted further up the kinetic chain.
Diagnosis
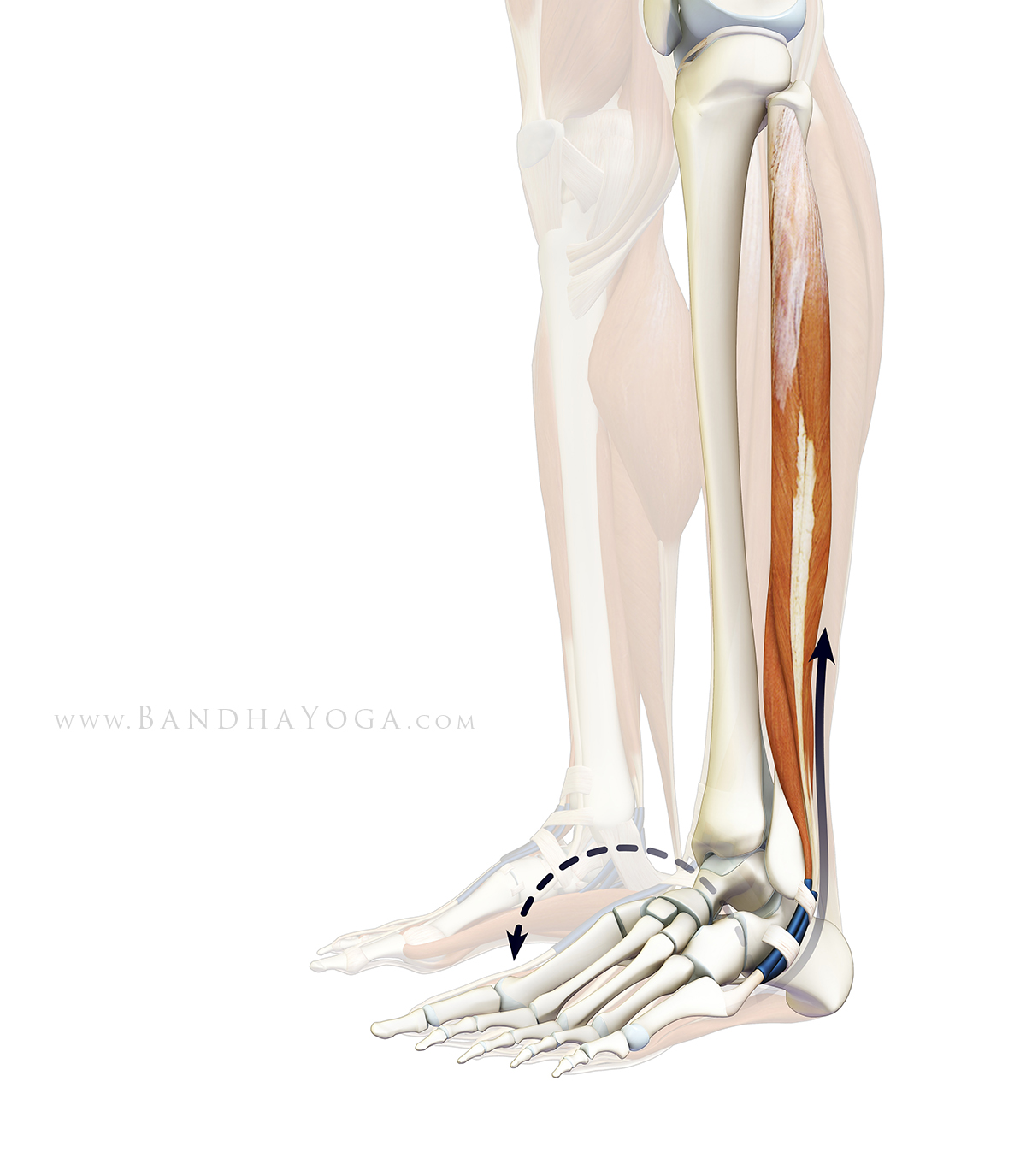
You can test for pronation by looking at the leg and foot from the back. Normally you can see the Achilles Tendon run straight down the leg into the heel. If the foot is pronated, the tendon will run straight down the leg, but when it lies on the heel it will twist outward. This makes the inner ankle bone much more prominent than the outer ankle bone.

Non Surgical Treatment
The following exercises help retrain the foot and ankle complex to correct overpronation. Step Up and Over. This exercise is designed to integrate skills learned in the Duck Stand, Big Toe Pushdowns and Side Step with Opposite Reach exercises to mimic walking and even running. Using the gluteal muscles and big toe in tandem will prevent overpronation while moving back and forth over the BT in a more effective, balanced motion. Movement Directions. Stand with left foot on top of the BT dome. (Note: For added balance, the right foot can tap on the ground, if needed). Extend right foot backwards to the ground and drop hips into a lunge position. Make sure that the right arm rotates across the left leg (this will activate the gluteal muscles on the left side). Now, step through and over the BT into a front lunge with the right leg forward. While lunging forward, the torso and left arm now rotate over the right leg. Throughout the exercise, push big toe down into the BT. Perform 8 to 10 repetitions on both sides.
Prevention
Duck stance: Stand with your heels together and feet turned out. Tighten the buttock muscles, slightly tilt your pelvis forwards and try to rotate your legs outwards. You should feel your arches rising while you do this exercise.
Calf stretch:Stand facing a wall and place hands on it for support. Lean forwards until stretch is felt in the calves. Hold for 30 seconds. Bend at knees and hold for a further 30 seconds. Repeat 5 times.
Golf ball:While drawing your toes upwards towards your shins, roll a golf ball under the foot between 30 and 60 seconds. If you find a painful point, keep rolling the ball on that spot for 10 seconds.
Big toe push: Stand with your ankles in a neutral position (without rolling the foot inwards). Push down with your big toe but do not let the ankle roll inwards or the arch collapse. Hold for 5 seconds. Repeat 10 times. Build up to longer times and fewer repetitions.
Ankle strengthener: Place a ball between your foot and a wall. Sitting down and keeping your toes pointed upwards, press the outside of the foot against the ball, as though pushing it into the wall. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times.
Arch strengthener: Stand on one foot on the floor. The movements needed to remain balanced will strengthen the arch. When you are able to balance for 30 seconds, start doing this exercise using a wobble board.